Corvette Generations:
C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8
Corvette: Year by Year
1953 1954 1955 1956 1957 1958 1959 1960 1961 1962 19631964 1965 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970 1971 1972 1973 1974
1975 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984 1985
1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996
1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018
2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025
1984 Corvette C4 Chassis Technology
A front grill, which had gradually been disappearing as the Corvette progressed, was gone completely in the C4. Some judicious engineering resulted in adequate airflow ducted from under the car for the radiator to cool the engine. Replacing the grill was a set of halogen running lamps, an inspiration gained from comparisons to the Porsche 928 and other european cars of the time. Cornering lamps located behind the front side marker lights were standard.
Note also that the new Corvette had almost a "bumperless" design. Although functional in that the bumpers protected the car from up to 5 mph of harm, they were also integrated fully into the body shape so that it was not possible to point out where the bumpers/body were defined.
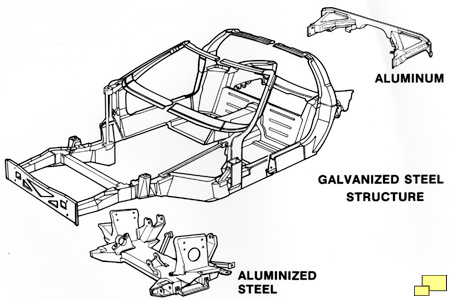
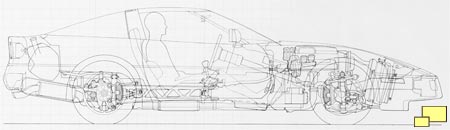
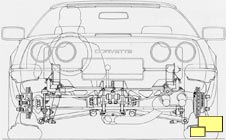
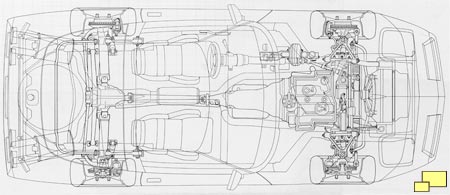
Light weight was a primary engineering goal which was achieved with generous amounts of aluminum in the suspension and chassis parts. Aluminum alloy was used in the half shafts, differential support, front and rear suspension crossmembers, drive shaft, torque convertor / transmission housing and various mounting brackets. The use of light weight materials in suspension parts was used to reduce unsprung weight which is necessary in a good handling world class sports car. Other benefits include more consistent parts with a die cast process, freedom from rust and they just look awesome.
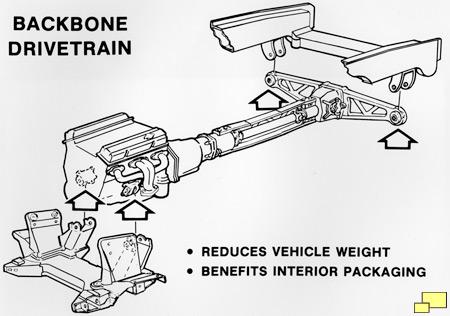
A aluminum "C" section channel beam connected the transmission and the differential. Firmly tying together the major front (engine/transmission) and rear (differential and rear suspension) components improved handling and makes for a tight and agile driving feel. It's a common method used in other quality handling cars such as the Mazda Miata.
The transverse leaf spring which had worked so well in the rear suspension of all Corvettes since 1963 was part of the C4 design for both the rear and front suspension. A new design was made up of a single leaf (as opposed to multiple leafs) using fiberglass reinforced epoxy resin plastic. The innovative system resulted in lower unsprung weight and increased reliability. According to Chevrolet, the new fiberglass springs could be exercised 5,000,000 times without failure while the steel equivalent would usually break after about 750,000 jounces.
The C2 and C3 rear suspension, although fully independent, was still a relatively simple three link design. The C4 got a bit more sophisticated with a five link rear suspension.
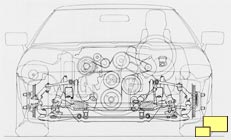
At the front suspension, another Corvette first appeared: rack and pinion steering. It was the same system used in other great sports cars and was known for quick response and accuracy. A small damper was added to improve steering feel. The standard ratio was a relatively quick 15.5:1; an even faster ratio (13.0:1) was part of the performance handling package (RPO Z51; $600.20).
Next: 1984 Corvette C4 Handling, G-Forces, Squeaks and Rattles
1984 Corvette C4 New Look, Front Engine
1984 Corvette C4 Targa Roof, Engine Access
1984 Corvette C4 Handling, G-Forces, Squeaks and Rattles
1984 Corvette C4 Upgrades, Interior, Instruments, Sound System