Corvette Generations:
C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8
Corvette: Year by Year
1953 1954 1955 1956 1957 1958 1959 1960 1961 1962 19631964 1965 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970 1971 1972 1973 1974
1975 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984 1985
1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996
1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018
2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025
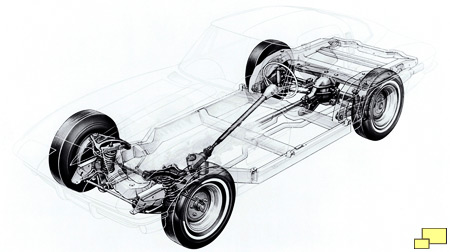
1963 Chevrolet Corvette C2 Chassis
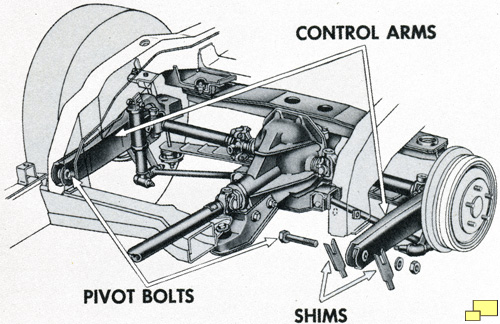
Designed by Zora Arkus-Duntov, a independent rear suspension (IRS) was part of the new chassis. This was a bold move on the part of GM. To put it into perspective, consider this. It wasn't until 1992 - 29 years - after the introduction of the 1963 'vette that a car with an IRS designed by Chrysler (the 1992 Viper) was available to the public.
Almost all cars of the time, including the C1 Corvettes, used a live rear axle as the major part of the rear suspension. It's a simple and economical solution that works well in most cases. But the live axle has two problems when used in high performance handling applications.
- It is heavy. When designing a performance handling car, engineers will go to great lengths to reduce unsprung weight; that is the weight of the wheels and the associated suspension parts that they are connected to. Less weight means that it is easier to control the wheels which means that the tires contact the road surface more consistently. A live rear axle has the heavy differential connected to the wheels. With an IRS the differential is bolted to the frame and not part of the unsprung weight.
- The IRS deals with rough surfaces better. When a bump or surface irregularity is encountered by a wheel, it does not affect the other wheel. The result is that the tire on the side that did not hit the bump maintains a consistent contact with the road.
It is worth noting that the 1963 C1 Corvette chassis was used, mostly unchanged, until the 1982 Corvette - 20 model years - a testimony to the soundness of the design.
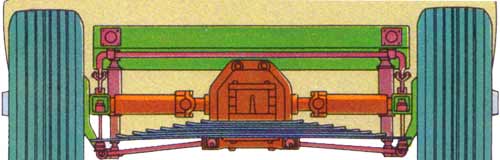
The extra complexity adds to the manufacturing costs, so keeping it simple was a necessity. An ingenious single multi-leaf transverse spring accommodated both wheels, kept costs under control and featured low unsprung weight. Overall weight was down by about 100 lbs. when compared to the previous straight axle design.
Click here to download the 1963 Corvette Rear Suspension manual.
The IRS was a radical move and positioned the Corvette as a serious road car. The improvement was dramatic and car enthusiasts from all backgrounds took notice. Overall, the handling was much better and so was the feel. The new Corvette was not only faster on the race track, it also felt better. By comparison, the earlier Corvettes felt more cumbersome. The steering feel, agility, responsiveness and "fun to drive" factor was such that even foreign car aficionados took notice.
Next: 1963 Corvette - Glory Years, Split Window Coupe
1963 Corvette C2 - The Most Significant Corvette
1963 Corvette - Sting Ray, Engine Selection
1963 Corvette - Interior, Hidden Headlights
1963 Corvette - Production Quantities, Wheel Choices
1963 Corvette - Brochure, GM photographs
1963 Corvette Z06
1963 Corvette SAE Paper
1963 Corvette Specs