Corvette Generations:
C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8
Corvette: Year by Year
1953 1954 1955 1956 1957 1958 1959 1960 1961 1962 19631964 1965 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970 1971 1972 1973 1974
1975 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984 1985
1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996
1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018
2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025
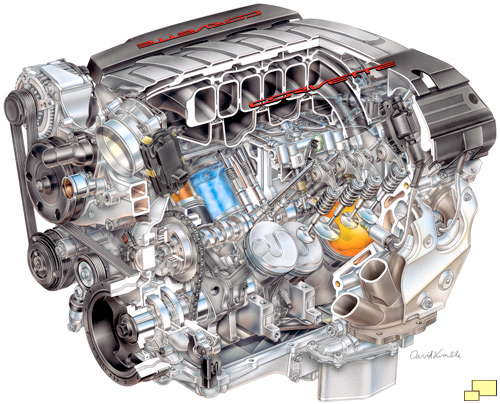
Corvette C7 Engine
The new engine was the fifth generation of what the automotive enthusiast world has come to know and love as the "Small Block Chevy" of which over 100,000,000 have been built. First available in 1955, the "Gen 5" shares a few characteristics with it's seemingly ancient compadre: A V8 configuration, two valves per cylinder, a single camshaft located in the middle of the block and 4.40 inch cylinder bore centers.
 Direct Injection
Direct Injection
DI made its debut on the C7 Corvette motor. The technique injects fuel directly into the combustion chamber as opposed to the valve chamber as in previous generation Corvette motors, a technique that allowed the compression ratio to be raised to 11.5:1; previously it was 10.7. It is largely responsible for the significant gains in fuel economy as well as horsepower. Direct injection also keeps the combustion chamber cooler, which allows for a higher compression ratio. Emissions are lower, including the all-important cold start hydrocarbons which was cut by 25%.
Fuel economy is kept under control by shutting down four of the cylinders during subdued driving conditions, turning the LT1 6.2 L V8 into a 3.1 L V4. Cylinder shutdown is accomplished by deactivating the lifters in cylinders 1, 4, 5 and 6. V4 operation, in the case of manual transmission C7 Corvettes, is only available in the Eco mode. Output is a meager 125 horsepower.
 Variable Valve Timing
Variable Valve Timing
The LT1 camshaft is in the same position as that found in the original small block motor introduced in 1955 - in the center of the block. The new complex camshaft supports variable valve timing, giving the LT1 engine three camshaft profiles to choose from. The result is increased performance and fuel economy along with reduced emissions. It also drives the engine-mounted direct injection high-pressure fuel pump, which powers the direct-injection combustion system. The cam’s specifications include 14mm/13.3mm intake/exhaust lift, 200/207-crank angle degrees intake/exhaust duration at 1.3mm tappet lift and a 116.5-degree cam angle lobe separation.
Horsepower is 460 @ 6,000 RPM, Torque is 465 lb-ft @ 4,600 RPM (Dual mode performance exhaust included, RPO NPP). Max RPM is 6,600 RPM; go beyond and an automatic fuel cutoff comes into effect. Left: LT1 engine on the dynamometer.
Fuel Economy
The 2014 Corvette has been rated by the EPA as getting 16 mpg city / 28 mpg highway / combined 20 mpg (automatic transmission) and 17 mpg city / 29 mpg highway / combined 21 mpg (manual transmission). Premium unleaded fuel is required. Like every Corvette (except for the 2009 thru 2013 ZR1) since the rating system was implemented, the 2014 Corvette is not subject to a gas guzzler tax.